The motherboard is the central nervous system of your PC—it connects and powers every component. But to new PC builders, a motherboard can look like a maze of weird slots, pins, and acronyms.
In this two-part guide, we’ll break down the essential parts of a motherboard, explain what each section does, and help you confidently plug in your CPU, GPU, RAM, SSDs, fans, and more.
Form Factor – The First Thing to Know
Before diving into ports and pins, you should know the size and layout of your motherboard.
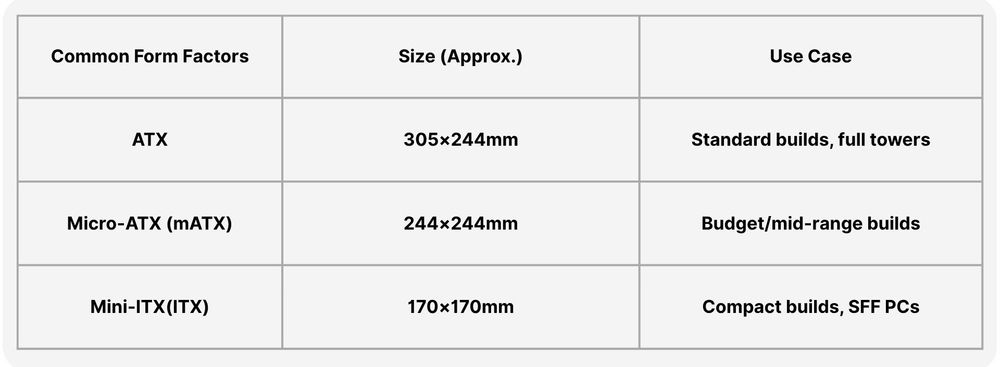
Tips: Make sure your PC case supports the motherboard size you choose.
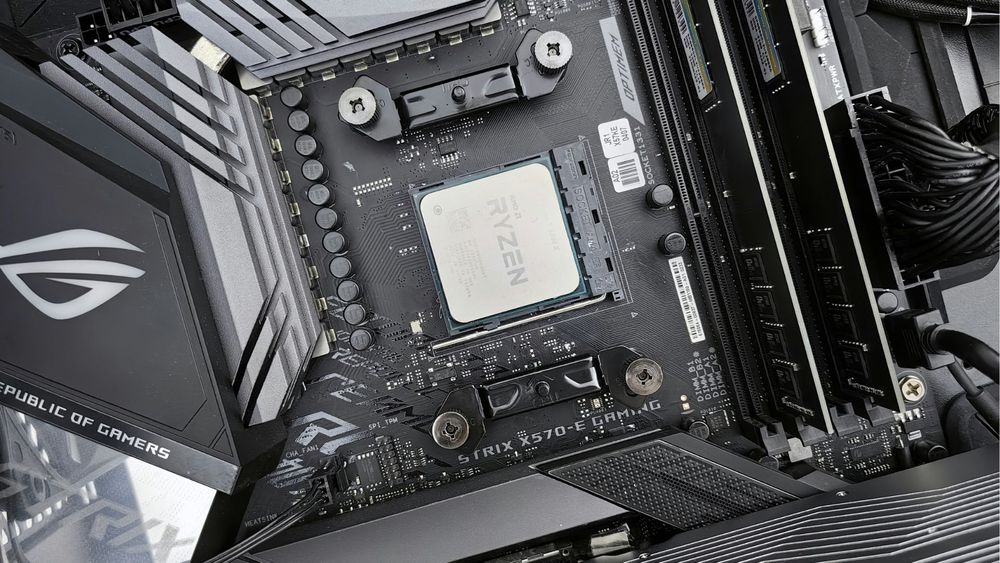
CPU Socket – The Master Mind
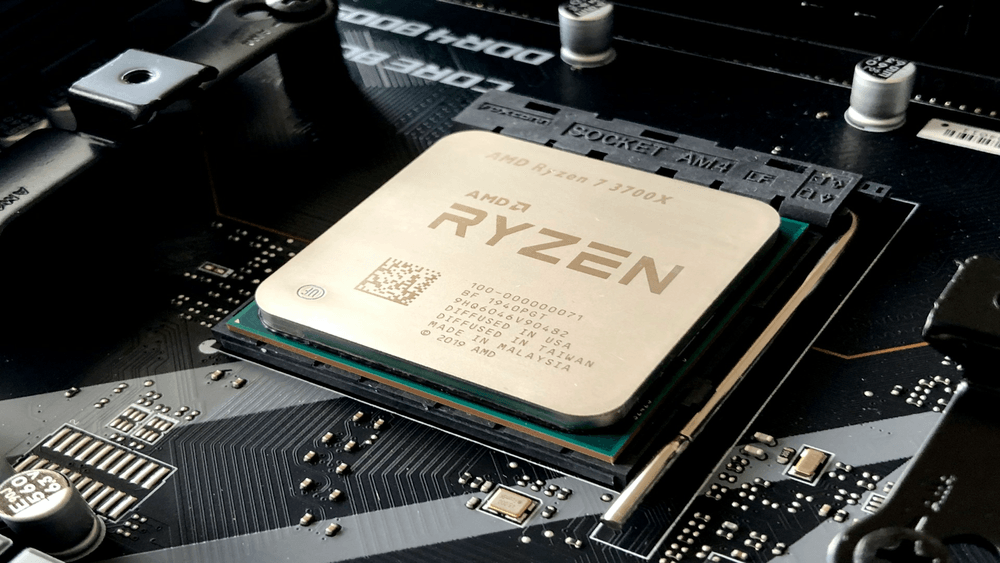
This is where your processor (CPU) goes. It’s a square-shaped socket with a latch.
Intel: LGA 1851, LGA 1700, etc. (pins are on the motherboard)
AMD: AM4, AM5 (pins are on the CPU)
Beware: You must match the CPU socket type with your processor model.
Tips: Most motherboards also have a VRM heatsink near the CPU socket for power regulation.
RAM Slots – Memory Matters
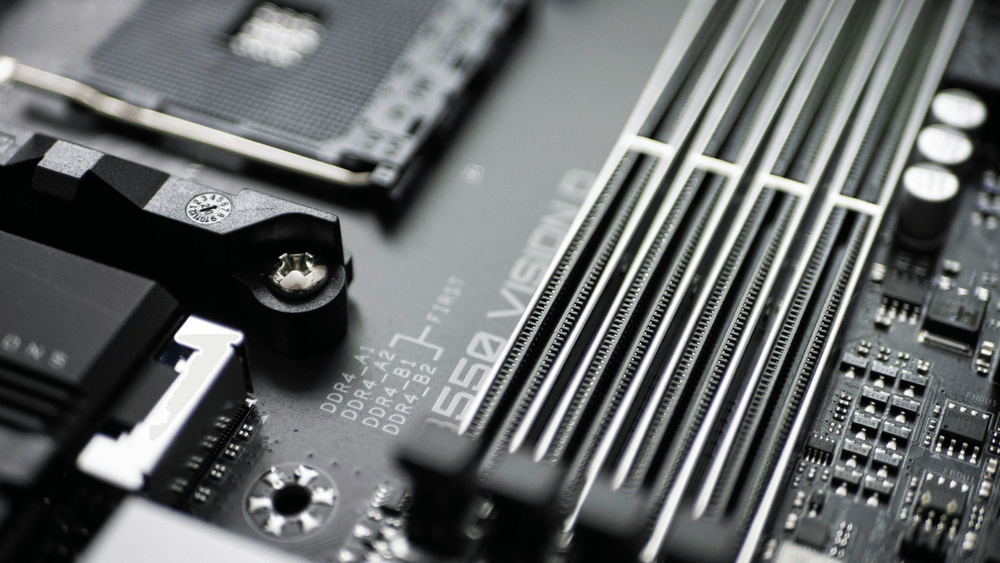
These are the long vertical slots beside the CPU socket.
Labeled as DIMM1, DIMM2, etc.
Usually 2 or 4 slots depending on board size
Only supports DDR4 or DDR5 (not both!)
Tips: Install RAM in the correct slots for dual-channel (usually slots 2 and 4 counting from the CPU side – check the manual).
PCIe Slots – For Graphics Cards and More
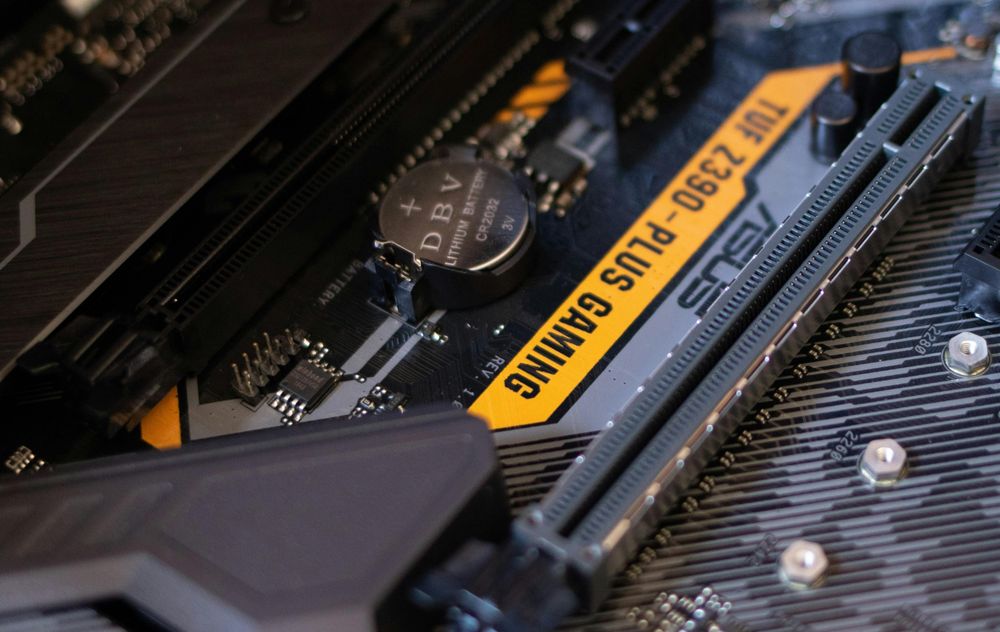

These are the horizontal slots under the CPU area. With the longer one supporting up to PCIex16 usually for graphics cards and the shorter one for Capture cards, Wi-Fi, sound cards. Newer motherboards may support PCIe Gen 5.0, but GPUs still mostly use Gen 4.0.
Tips: Use the top PCIe x16 slot for your GPU—it’s wired with the most bandwidth.
M.2 and SATA – Storage Interfaces
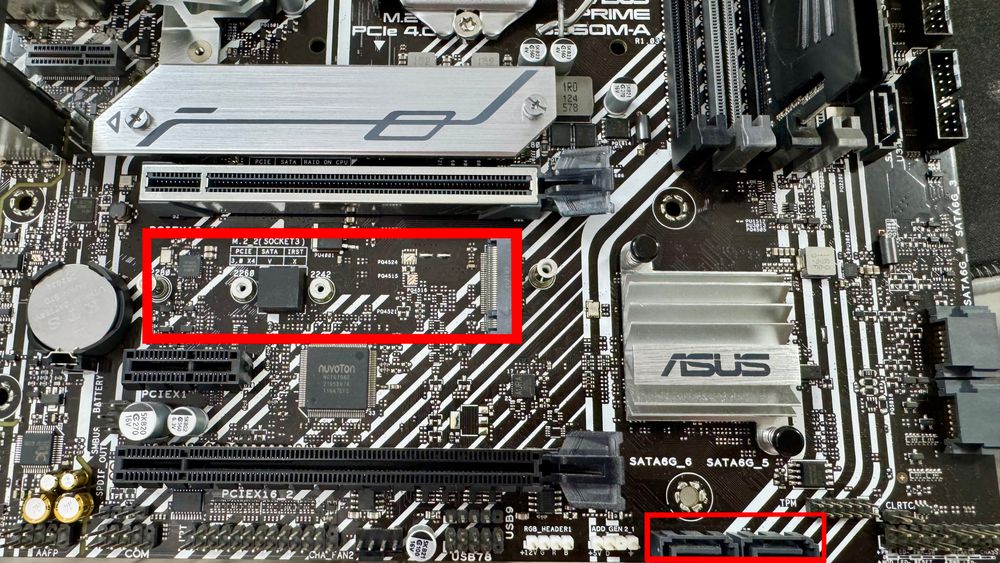
Modern motherboards come with M.2 slots and SATA ports.
M.2 Slots (for NVMe or SATA SSDs):
Typically located between PCIe slots
Look for labels like M.2_1, M.2_2
May need to remove a heatsink
SATA Ports (for 2.5" SSDs, HDDs):
Usually 4–6 L-shaped connectors on the edge
Tips: Some M.2 slots disable SATA ports when in use—check the manual.
What's Next?
In the next post, we will walk you through the other side of the motherboard—SATA ports, power connectors, front I/O, fan headers and more! Stay tuned so you can master every inch of your motherboards before you build.